As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Different Purposes of Resonator And Catalytic Converter?
Resonators are used to reduce noise, while catalytic converters help to lower harmful emissions. Resonators and catalytic converters serve different purposes in vehicle exhaust systems.
Resonators are designed to reduce noise levels in the exhaust system, while catalytic converters help to lower harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances. Understanding the functions of these components is essential in maintaining the performance and efficiency of a vehicle.
We will explore the distinct roles that resonators and catalytic converters play in the exhaust system, as well as their impacts on vehicle performance and environmental considerations. Let’s dive into the details of how these components work and why they are crucial for ensuring a cleaner and quieter driving experience.
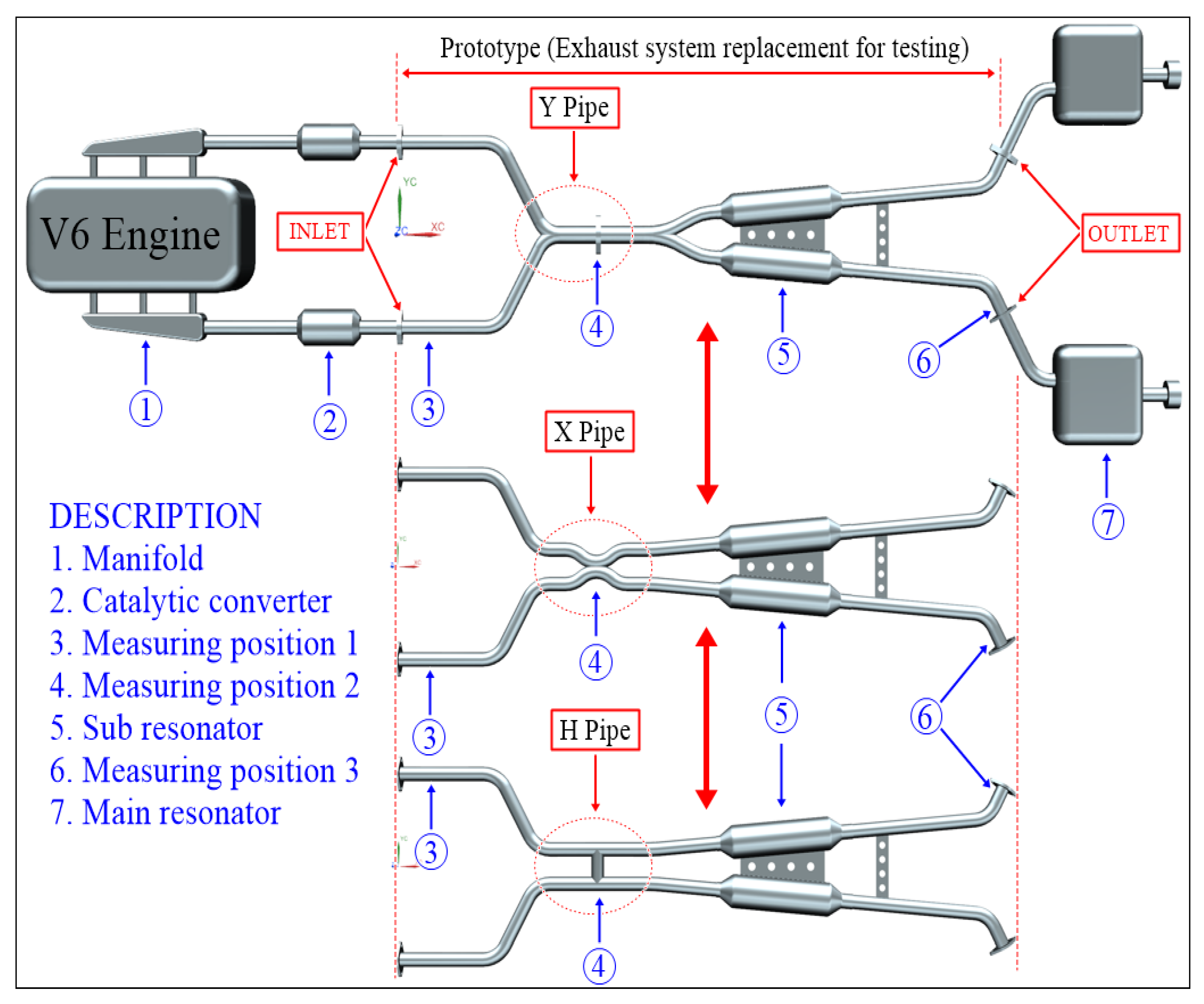
Credit: www.mdpi.com
What Is A Resonator?
A resonator is a component of a vehicle’s exhaust system designed to minimize noise levels, enhance engine performance, and reduce exhaust emissions. It acts as a soundproofing device to eliminate unpleasant engine noise.
Definition
A resonator is a chamber or box-like component found in the exhaust system, often located between the catalytic converter and the muffler. It is typically constructed from stainless steel or aluminum to withstand the high-temperature conditions within the exhaust system.
Function
The primary function of a resonator is to cancel out certain frequencies of sound produced by the engine, resulting in a quieter overall exhaust note. It achieves this by utilizing a process called acoustic resonance, which neutralizes the sound waves radiating from the engine.
Benefits Of A Resonator
Resonators play a crucial role in the exhaust system of a vehicle, offering various advantages. Let’s dive into the benefits of a resonator below:
Noise Reduction
Resonators are designed to reduce the loud noise produced by the exhaust system, resulting in a quieter driving experience.
Improved Engine Performance
A resonator helps in enhancing the overall engine performance by reducing back pressure and allowing smoother airflow.
Types Of Resonators
Resonators serve various functions, including reducing noise and improving engine performance in vehicles. On the other hand, catalytic converters help to minimize harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances. Both components play crucial roles in enhancing the overall efficiency and environmental impact of automobiles.
Acoustic Resonator
An acoustic resonator enhances sound quality and minimizes noise in the exhaust system.
Helmholtz Resonator
A Helmholtz resonator reduces specific frequencies for improved engine performance.
Tuned Resonator
A tuned resonator optimizes exhaust airflow for better fuel efficiency and power output.
Resonators in a vehicle’s exhaust system serve different purposes, from minimizing noise level to enhancing engine performance. These technologies are crucial for maintaining engine efficiency and meeting emission standards.
Credit: www.quora.com
What Is A Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic converter is a crucial component in a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce harmful emissions before they are released into the environment. This device plays a major role in reducing air pollution caused by vehicle exhausts, making it an essential part of modern vehicles.
Definition
A catalytic converter is a vehicle emissions control device that converts toxic pollutants in exhaust gas to less toxic substances by catalyzing a redox reaction.
Function
- Emission Reduction: The primary function of a catalytic converter is to decrease the harmful emissions produced by the vehicle, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides.
- Catalyzing Reaction: It facilitates a chemical reaction wherein the harmful gases are converted into less harmful compounds, such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen.
Importance Of A Catalytic Converter
The Catalytic Converter plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions from a vehicle, while the Resonator helps to diminish engine noise. Together, these components aid in improving air quality and creating a quieter driving experience.
A catalytic converter is a crucial component in a vehicle’s exhaust system, primarily designed to reduce harmful emissions. It plays a vital role in minimizing the environmental impact caused by the combustion process in an internal combustion engine.
Reducing Emissions
One of the primary purposes of a catalytic converter is to reduce emissions. When the fuel is burned in the engine, harmful gases such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons are released. These pollutants contribute to air pollution and have adverse effects on human health.
The catalytic converter contains a catalyst, typically made up of precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which facilitate chemical reactions. This catalyst converts the toxic gases into less harmful substances through oxidation and reduction reactions.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of vehicle emissions is a growing concern worldwide. The emission of pollutants contributes to the greenhouse effect, leads to climate change, and affects the overall air quality.
A properly functioning catalytic converter helps in reducing these emissions by converting harmful gases into less harmful substances. This significantly helps in improving air quality and minimizing the negative impact on the environment.
A catalytic converter is not only necessary for meeting governmental regulations and emission standards but also to ensure a clean and sustainable environment for future generations.
Credit: www.thedrive.com
Types Of Catalytic Converters
In the realm of exhaust emission control systems, catalytic converters play a crucial role. They help reduce harmful gases emitted by vehicles and ensure a cleaner environment. There are different types of catalytic converters that serve specific purposes in the emission control process. Let’s explore three commonly used types of catalytic converters:
Three-way Catalyst
The three-way catalyst, also known as TWC, is one of the most prevalent types of catalytic converters used in the automotive industry. Its primary function is to reduce three major pollutants: nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrocarbons (HC), into less harmful substances.
TWC contains two main components: a reduction catalyst and an oxidation catalyst. The reduction catalyst helps convert nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) gases. Simultaneously, the oxidation catalyst transforms carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O).
The three-way catalyst is effective in reducing multiple harmful gases and plays a vital role in meeting stringent emission regulations.
Oxidation Catalyst
An oxidation catalyst, as the name implies, focuses primarily on converting carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). This type of catalytic converter is commonly used in gasoline engines, especially those without a surplus of nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions.
Oxidation catalysts consist of precious metals, such as platinum and/or palladium, which facilitate the oxidation reaction. These metals act as catalysts, promoting the conversion of carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances.
Due to its specific function, the oxidation catalyst is often used in conjunction with other technologies, such as Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs), to achieve comprehensive emission control.
Conclusion
Resonators and catalytic converters serve distinct yet crucial functions in a vehicle’s exhaust system. While resonators minimize noise, catalytic converters clean harmful emissions. Understanding their unique roles can help ensure efficient and effective performance of your vehicle, enhancing overall environmental and mechanical benefits.
Choose wisely!


